KuppingerCole's Advisory stands out due to our regular communication with vendors and key clients, providing us with in-depth insight into the issues and knowledge required to address real-world challenges.

Unlock the power of industry-leading insights and expertise. Gain access to our extensive knowledge base, vibrant community, and tailored analyst sessions—all designed to keep you at the forefront of identity security.
Get instant access to our complete research library.
Access essential knowledge at your fingertips with KuppingerCole's extensive resources. From in-depth reports to concise one-pagers, leverage our complete security library to inform strategy and drive innovation.
Get instant access to our complete research library.
Gain access to comprehensive resources, personalized analyst consultations, and exclusive events – all designed to enhance your decision-making capabilities and industry connections.
Get instant access to our complete research library.
Gain a true partner to drive transformative initiatives. Access comprehensive resources, tailored expert guidance, and networking opportunities.
Get instant access to our complete research library.
Optimize your decision-making process with the most comprehensive and up-to-date market data available.
Compare solution offerings and follow predefined best practices or adapt them to the individual requirements of your company.
Configure your individual requirements to discover the ideal solution for your business.

Meet our team of analysts and advisors who are highly skilled and experienced professionals dedicated to helping you make informed decisions and achieve your goals.

Meet our business team committed to helping you achieve success. We understand that running a business can be challenging, but with the right team in your corner, anything is possible.
In this Leadership Compass, we evaluate customer data platforms.
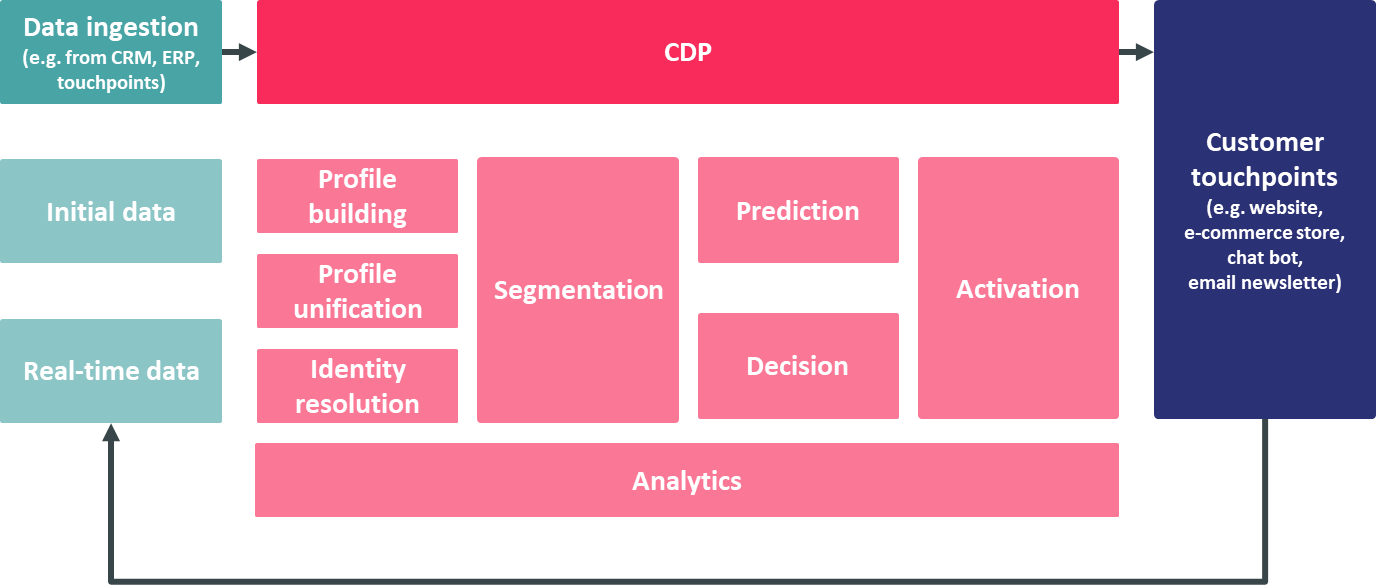
The term "customer data platform," or CDP, stands for software (or a collection of software) that creates databases that enable the centralized management of customer data.
Organizations across all industrial sectors face the challenge of their customers expecting a seamless customer journey across various analog and digital touchpoints. This comprises highly individual marketing messages, recommendations, and the right information at the right point in time.
Due to scattered data silos, it is a challenge for most organizations to create 360-degree customer profiles, build customer segments, or manage customer journeys based on complete customer-related information.
Customer data platforms can help in such cases to break down data silos, aggregate information, and create compete customer profiles and segments as a basis for integrated omni-channel customer experiences across all touchpoints by connecting to first- and third-party solutions in best-of-breed technology stacks.
Thus, this Leadership Compass analyzes CDP solutions on the market to give an overview of the market positions of the vendors and the functionality of the solutions itself, with a focus on the following key aspects:
In addition, this Leadership Compass evaluates the capabilities of the solutions in terms of security, functionality, deployment models, interoperability, and usability.
The graphic below illustrates the typical functionality of a CDP, starting with data ingestion based on various sources: