Oracle Access Governance is a cloud-native IGA solution which runs in Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI). Oracle Access Governance can also run alongside Oracle Identity Governance in a hybrid deployment model to provide identity analytics from the cloud for Oracle Identity Governance customers. It serves as a one-stop shop for identity orchestration, user provisioning, access review, access control, compliance, and multi cloud governance. It offers a mobile-friendly, cloud-native governance solution. It can detect and remediate high-risk privileges by enforcing internal access audit policies to identify orphaned accounts, unauthorized access, and privileges. This helps improve compliance with regulatory requirements. With the capacity to manage millions of identities, Oracle suggests it is suitable for enterprise level organizational needs.
User Provisioning
Setting up this governance solution has two options. It can be done through connectors for systems easily accessible and for disconnected applications that cannot directly connect with Oracle Access Governance or are behind firewall systems, Oracle provides a one-time connector which can be downloaded by the administrator. The connector establishes the integration with the target system to securely sends and receives encrypted data to Oracle Access Governance. The connector continuously polls for access remediation decisions from Oracle Access Governance. The user interface provides detailed status updates for each connected system, including data load status and duration. In the latest update, Oracle Access Governance introduces new capabilities that focus on provisioning, identity orchestration, identity reconciliation and prescriptive analytics.
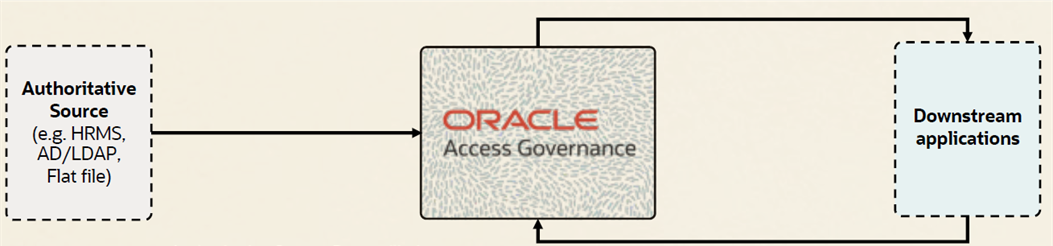
Figure 1: Identity provisioning and reconciliation
Oracle Access Governance’s identity orchestration makes use of identity provisioning and reconciliation capabilities along with schema handling, correlation, and transformations. The update provides comprehensive features for account provisioning by allowing users to create accounts by leveraging outbound transformation rules and assigning them appropriate permissions to access downstream applications and systems. The Access Governance platform can also perform reconciliation by synchronizing user accounts and their permissions from integrated applications and systems. Oracle suggests this will also support handling ownership to reduce orphan and rogue accounts effectively. Oracle suggests business owners can either manually address these orphaned accounts or allocate orphaned accounts to specific identities, followed by regular review cycles for these assigned accounts. Additionally, event-based reviews can be set up to automatically assess rogue and orphaned accounts as soon as they are detected within an integrated application or system.
Oracle’s Access Governance platform can also support authoritative source reconciliation from systems such as HRMS, AD, LDAP for onboarding, updating, and deleting identities through identity reconciliation. This solution combines identity provisioning and reconciliation capabilities, supported by robust integration. Whether it's for on-premises or cloud-based workloads, Oracle Access Governance offers a reliable framework for managing identity and access effectively.
Access reviews
Oracle Access Governance offers intelligent access review campaigns using AI and ML driven prescriptive analytics for periodic and micro certifications. These analytics provide insights and recommendations to proactively manage access governance and ensure compliance effectively.
Oracle Access Governance offers a robust suite of features for access review for management of user permissions. The solution has manual access review campaigns that provides admins with a wizard-based interface for campaign creation. Oracle has also leveraged machine learning for managing reviews by providing deep analytics and recommendations. Oracle suggests that this will simplify the approval and denial of access. The platform also offers flexibility of scheduling periodic access review campaigns for compliance purposes. Oracle mentions this will streamline the process of auditing user permissions at regular intervals. Event-based micro certifications are also supported for limiting the certification of affected identities. Oracle has incorporated pre-built and customizable codeless workflows which are based on a simple wizard.
Moreover, administrators can set up ad hoc or periodic access review campaigns. The platform provides a granular approach for selecting criteria for access reviews. The identities can configure workflows according to their requirements or leverage AI and machine learning algorithms to suggest workflows based on certification history of related identities. The user interface for admins is modern and has features to review, download, and create reports on access review campaigns.
Conclusion
Oracle Access Governance continues to reinforce its identity and access management capabilities. With the ability to conduct micro-certifications instead of traditional certifications every six months, Oracle suggests their platform is well placed for streamlining governance procedures.
By leveraging cloud infrastructure, Oracle Access Governance is on track to support operations as well as facilitating integration with applications such as Cerner for auditing and compliance purposes. They plan monthly release cycle to their access governance platform with the latest features and enhancements. Oracle wants to provide visibility into access permissions across the enterprise using their dashboards which can be tailored based on requirements of business users. Furthermore, Oracle suggests this platform can be useful for CISOs by offering top-down or bottom-up consolidated views of access permissions across the enterprise.