When an organization uses a cloud service, it must make sure that it does this in a way that is secure and complies with their obligations. Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) provides a broad set of integrated cloud security services to help its customers achieve these objectives. Oracle continuously innovates to improve these services and Oracle Cloud Guard has now been enhanced to provide a complete Cloud Native Application Protection Platform (CNAPP) for OCI.
Complementary User Entity Controls
To meet their security and compliance obligations when using OCI the tenant must implement the appropriate controls. The American Institute of CPAs® (AICPA) provides attestations of the security and compliance of cloud services. OCI has a Service Organization Controls (SOC) 2 type 2 attestation that affirms that controls relevant to the AICPA Trust Services Security and Availability Principles are implemented effectively within OCI. This includes a consideration of the Complementary User Entity Controls (CUECs) that the OCI tenant is expected to implement as well as the capabilities provided by OCI to support these.
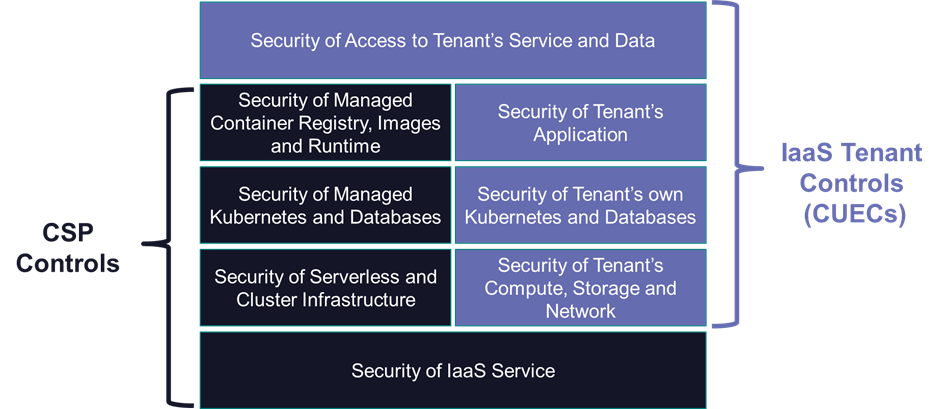
Figure 1: Complementary User Entity Controls
OCI offers a full stack of cybersecurity capabilities to help the tenant prevent, protect, monitor, and mitigate cyber threats and control access and encrypt data. These include Oracle Cloud Guard that was first launched in 2020 and enhanced in 2022 to provide Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM) for OCI. This detects misconfigurations, insecure activity, and threat activities and provides visibility to triage and resolve cloud security issues.
Oracle Cloud Guard CSPM, together with the other OCI security services, helps the OCI tenant to demonstrate how their CUECs meet their security and compliance objectives.
Oracle Cloud Guard for CSPM
Oracle Cloud Guard is an OCI service that helps OCI tenants to maintain a strong security posture on Oracle Cloud. The tenant can use the service to examine their OCI resources for security weakness related to their OCI configuration and monitor their OCI administrators for risky activities. When Cloud Guard detects weaknesses, it can identify appropriate corrective actions and assist in or automate implementing these.
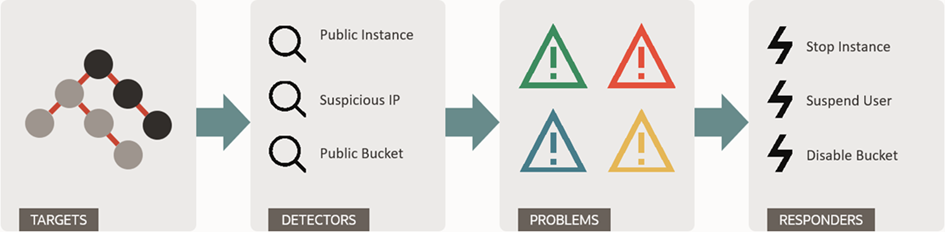
Figure 2: OCI CSPM Storage Bucket Risks Example
Cloud Guard detects security problems within a tenant OCI environment by ingesting activity and configuration data about their resources in each region, processing it based on detector rules, and correlating the problems at the reporting region level. Identified problems can be used to produce dashboards and metrics and may also trigger one or more inbuilt responders to help resolve the problem.
Oracle Cloud Guard works together with Oracle Security Zones to provide an always-on security posture. With Security Zones and Cloud Guard the OCI tenant can define policy compliance requirements for groups of resources. Security Zones and Cloud Guard can then enforce these policies to automatically correct and log any violations.
Cloud Security Posture Management is a valuable tool for organizations to ensure that they use OCI in a secure and compliant manner. OCI provides a very comprehensive range of capabilities for the tenant to secure their use of the services. Oracle Cloud Guard CSPM is one of these and is backed by the expertise and experience of Oracle’s technical teams.
Cloud Guard for CNAPP
The distinctive feature of CNAPP is the integration of several capabilities that were previously offered as standalone products. These most often include Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM) for identifying vulnerabilities and misconfigurations in cloud infrastructures, Cloud Workload Protection Platforms (CWPP) that deal with runtime protection of workloads deployed in the cloud (such as virtual machines, containers, and Kubernetes, as well as databases and APIs), and Cloud Infrastructure Entitlement Management (CIEM) for centralized management of rights and permissions across (multi-) cloud environments. Cloud Service Network Security (CSNS) is sometimes included as well, combining such capabilities as web application firewalls, secure web gateways, and DDoS protection. OCI Security Services include many of these capabilities.
Cloud Guard has provided CSPM capabilities since its launch in 2020. It has now been enhanced to offer further cloud native application security capabilities.
Cloud Guard Log Insights Detector
Cloud Guard Log Insights Detector, which is not yet generally available, provides a flexible way to capture specific events from logs available in the OCI Logging service. It allows customers to mine all their logs, augmenting out of the box controls to cover all resources and services.
It continuously monitors audit, service, and custom logs from Oracle IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS across all subscribed regions, and can be used to detect malicious events that may indicate a threat or a risk that needs to be investigated based on user-defined queries. Data from all services (like VCN flow logs, Object Storage or WAF), the OCI event audit trail and custom application logs can be accessed in every region, and results be centralized for consolidated alerting.
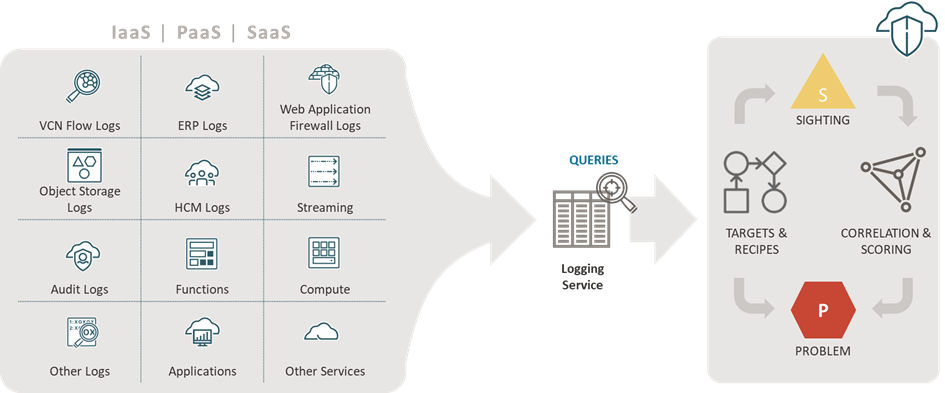
Figure 3: OCI Log Insights Detector
Cloud Guard Instance Security
This provides controls to manage risks and exposures at the compute server, microservices instance / container level. It detects suspicious runtime activities within OCI VMs based on MITRE ATT&CK and creates alerts in real time. It also monitors the integrity of critical system and application files. It comes with a range of predefined detection recipes, based on Oracle’s knowledge and OCI recommended best practices. These can be supplemented with ad hoc and custom scheduled queries.
Cloud Guard Container Security
Cloud-Native Applications are built using a microservices architecture based on containers. Microservices, containers, and Kubernetes have become synonymous with modern DevOps methodologies, continuous delivery, and deployment automation and are seen as a breakthrough in the way to develop and manage cloud-native applications and services.
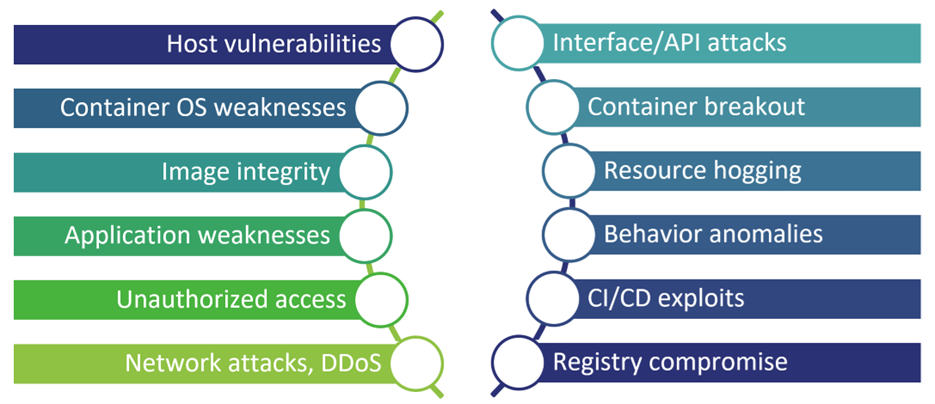
Figure 4: Examples of container related risks.
However, this approach brings new security challenges and attempts to repurpose existing security tools to protect containerized and microservice-based applications have proven to be inadequate due to their inability to adapt to the scale and ephemeral nature of containers. Static security products that focus on identifying vulnerabilities and malware in container images, while serving a useful purpose, do not address the full range of potential risks.
Oracle Kubernetes Engine (OKE) is an OCI platform for running Kubernetes workloads. Oracle Cloud Guard has been extended to include Kubernetes Security Posture Management (KSPM) for OKE. This helps to protect the DevOps pipeline processes and containers throughout their lifecycle from security vulnerabilities. It includes out-of-the-box configuration policies based on Oracle best practices. The rules also align with industry accepted best practices like CIS benchmarks and regulatory frameworks like US FedRAMP.
From CSPM to CNAPP
Since its inception in 2020 Oracle Cloud Guard has enabled OCI tenants to measure their security posture for OCI. These new capabilities extend Cloud Guard beyond CSPM to proactively manage the security of cloud native applications developed and deployed in OCI. This supports Oracle’s vision to make OCI the best platform for enterprises to develop and deploy secure and compliant applications. Organizations using OCI should review these new capabilities and adopt them where appropriate.